Application and Adaptation Scenarios of Thin-Wall Injection Molds in Food Packaging
With the rapid development of the takeaway economy and prepared food industry, coupled with the deepening implementation of environmental protection policies, the food packaging industry has witnessed a sustained surge in demand for lightweight, high-efficiency, and safety-compliant packaging products. Thin-wall injection molds, leveraging core advantages such as short molding cycles, high material utilization rates, and low production costs, have become the key production equipment for food packaging like fast food boxes, fresh-keeping containers, and cup lids. By precisely controlling the wall thickness (typically within the range of 0.2-1.5mm), they ensure the strength and sealing performance of packaging while achieving a significant reduction of 15%-30% in material loss, aligning with the green and efficient development direction of the food packaging industry. Currently, the application proportion of thin-wall injection molds in the food packaging field has exceeded 60% of the total plastic food container molds, and it continues to expand at an annual growth rate of 8.5%, serving as a crucial support for promoting the upgrading of the food packaging industry.
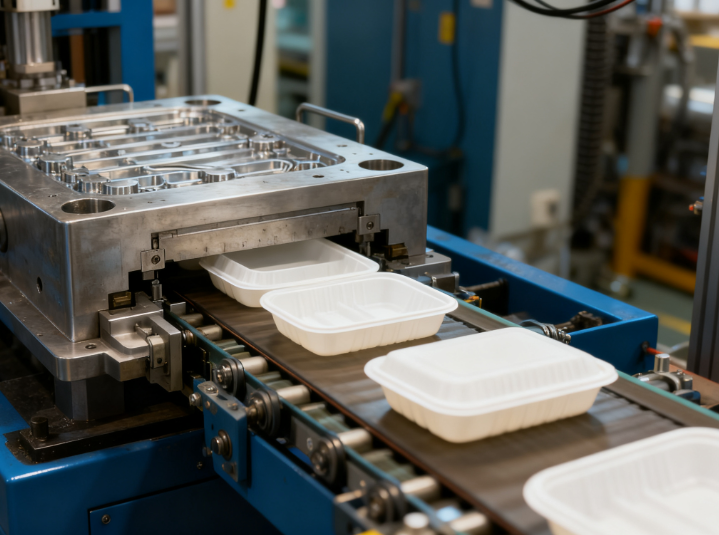

I. Core Application Scenarios of Thin-Wall Injection Molds in Food Packaging
(I) Production of Disposable Food Containers
Disposable fast food boxes, milk tea cups, takeaway trays, and other products are the main application carriers of thin-wall injection molds. Such packaging requires high-frequency and mass production. Through multi-cavity design (common 16-cavity, 32-cavity, and 64-cavity structures), thin-wall injection molds can shorten the single-product molding cycle to 10-25 seconds, increasing the daily production capacity by more than 40% compared with traditional molds. For common food-grade materials such as PP and PS, the mold optimizes the runner layout and cooling system to ensure the wall thickness uniformity error is controlled within ±0.05mm, avoiding insufficient load-bearing or microwave heating deformation caused by local excessive thinness.
(II) Manufacturing of Reusable Food Packaging
Reusable packaging such as fresh-keeping boxes and storage tanks has higher requirements for mold precision and durability. Thin-wall injection molds adopt mirror polishing technology (surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.02μm) combined with precision guiding mechanisms to ensure the dimensional tolerance of the product's sealing groove is controlled within ±0.01mm, meeting the sealing performance requirements of repeated opening and closing. For degradable materials such as PLA and PBAT, the mold adjusts the hot runner temperature curve and gate structure to solve the problems of poor fluidity and easy shrinkage of bio-based materials, promoting the large-scale production of environmentally friendly packaging.
(III) Molding of Special-Function Food Packaging
For special food packaging such as vacuum packaging trays for ready-to-eat food and prepared dishes, and microwave-heating special boxes, thin-wall injection molds need to integrate special functional structures. The in-mold insert technology realizes the uniform adhesion of anti-fog coatings, or the design of diversion grooves improves microwave heating efficiency. Such molds need to verify the structural rationality through spline testing to ensure the products have no deformation or peculiar smell under extreme environments from -20℃ freezing to 120℃ heating.
II. Core Content of Spline Testing for Thin-Wall Injection Molds Used in Food Packaging
(I) Design Requirements of Spline Testing Molds
Spline testing molds need to accurately simulate the core parameters of mass-produced molds, including key structures such as runner size, gate type, and cooling water channel layout. The mold cavity adopts standard spline dimensions (common 120mm×15mm×1mm standard splines), and reserves multiple sets of adjustable parameter interfaces to flexibly adjust process parameters such as hot runner temperature (range 160-240℃) and injection pressure (80-150MPa). The mold is equipped with temperature sensors and pressure sensors to collect key data during the molding process in real time, providing a basis for the optimization of mass production processes.
(II) Key Test Items and Judgment Standards
Wall thickness uniformity test: Use a laser thickness gauge to detect the wall thickness of different areas of the spline, and the error shall be ≤ ±0.03mm to ensure the uniform stress of mass-produced products.
Mechanical performance verification: Test the tensile strength (≥25MPa for PP materials, ≥18MPa for PLA materials) and elongation at break of the spline to avoid packaging damage during transportation.
Food contact safety test: Verify the release of heavy metals and volatile organic compounds from the spline through migration testing, complying with the requirements of GB 4806.7-2023 standard.
Molding stability test: Continuously produce 5,000 splines, and the defect rate shall be controlled within 0.3% to ensure the reliability of long-term mold operation.
(III) Mass Production Transformation and Application of Test Results
Spline test data directly guides the parameter optimization of mass-produced molds. For example, adjust the runner diameter according to the melt flow rate test results, or optimize the water channel layout based on the cooling uniformity data. For defects such as shrinkage and flash found in the test, adjusting the gate position or adding exhaust grooves can reduce the mass production defect rate by more than 60%. Spline testing molds can also be used for new material adaptation verification, shortening the R&D cycle of new packaging such as degradable materials by 30%-40%.
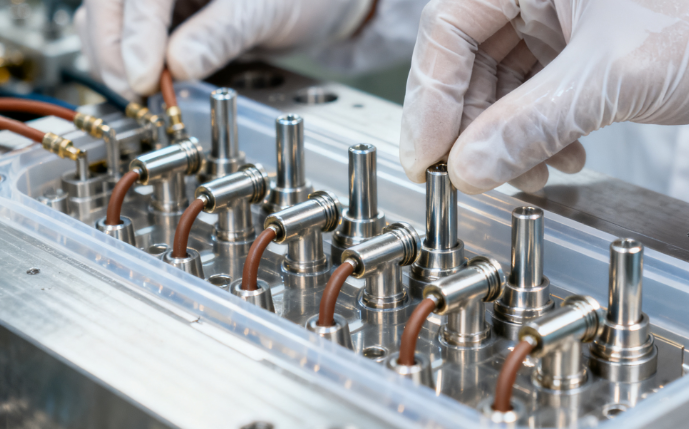

III. Adaptation Principles and Technical Trends of Thin-Wall Injection Molds
(I) Core Adaptation Principles
Material adaptation: Select mold steel and hot runner system according to the characteristics of packaging materials. P20 pre-hardened steel is suitable for general-purpose materials such as PP and PS, while S136 corrosion-resistant steel is preferred for degradable materials.
Structural adaptation: Adopt multi-cavity parallel design for rigid packaging (such as food boxes), and optimize the demolding mechanism for flexible packaging (such as cup lids) to avoid product deformation.
Production capacity adaptation: Choose 16-32 cavity molds for small and medium-batch production, and 64-128 cavity stack molds for mass orders to balance production capacity and cost.
(II) Current Technical Development Trends
Intelligent integration: Molds are equipped with industrial Internet modules to realize real-time monitoring of molding parameters and remote fault diagnosis, with the equipment networking rate of leading enterprises reaching 68.4%.
Green upgrading: R&D of special molds for degradable materials is accelerating. In 2024, related technical patents increased by 36% year-on-year, and the mold service life was extended to more than 800,000 cycles.
Precision improvement: The popularization of five-axis linkage machining technology has evolved the mold precision to ±0.005mm, meeting the aesthetic and functional requirements of high-end food packaging.
(III) Practical Production Adaptation Suggestions
Manufacturing enterprises should select molds based on packaging type, material characteristics, and production capacity requirements, and prioritize mold solutions verified by spline testing. For high-value-added products, mold flow analysis software (such as Moldflow) can be introduced for preliminary simulation to reduce the number of test molds; for mass production, it is recommended to use molds with quick mold change mechanisms to shorten production switching time. At the same time, a regular mold maintenance mechanism should be established, focusing on inspecting the hot runner system and guiding mechanism to extend the mold service life.
The application of thin-wall injection molds in the food packaging industry has evolved from a simple production tool to an integrated solution of "material-structure-production capacity". In the future, with the deep integration of digital design and green material technology, their adaptation scenarios in prepared food packaging, high-end food containers and other fields will be further expanded.
