In the field of material testing and precision manufacturing, spline test molds serve as core equipment for verifying material mechanical properties, molding quality, and working condition adaptability. Polishing and nitriding, two key surface modification technologies, endow these molds with distinct functional characteristics and application scenarios. Polishing spline test molds provide high-precision carriers for material appearance molding and demolding performance testing through ultra-high surface accuracy, while nitrided spline test molds adapt to harsh-condition material testing via enhanced surface hardness and corrosion resistance. According to 2024 domestic precision mold market reports, the combined application ratio of these two mold types in new energy vehicles, electronic information, and high-end equipment manufacturing exceeds 65%, with accelerating technological iteration driven by rising material R&D precision demands. This article systematically analyzes their core features from structural composition, design key points, performance-scenario matching, manufacturing and operation specifications, and technological trends, offering technical support for practical production and testing.
Despite differing surface treatment processes, both mold types share a common structural framework comprising five components, with material selection and functions tailored to their respective processes:
Mold Base: Constructed from S50C high-quality carbon structural steel for rigidity and processability. Polishing mold bases require guide accuracy within 0.005mm to maintain cavity polishing precision, while nitrided mold bases reserve 0.1-0.2mm machining allowance for nitriding layers.
Cavity and Core: As core molding components, polishing molds adopt S136 corrosion-resistant mold steel (achieving Ra0.008μm mirror finish), while nitrided molds use 38CrMoAl alloy steel (surface hardness reaching HRC65+ post-nitriding). Cavity dimensions comply with GB/T 1040.2-2006 standards with ±0.01mm tolerance.
Cooling System: Polishing molds feature uniformly distributed water channels (20-30mm spacing, ±1℃ water temperature fluctuation) to prevent uneven shrinkage. Nitrided molds use high-temperature seals and 1-2mm enlarged water channels for improved heat dissipation.
Runner System: Polishing molds employ 1.5-2mm pin gates to minimize flash. Nitrided molds for metal stamping integrate lubrication channels to avoid material adhesion.
Design focuses on surface precision control and demolding stability:
Cavity Surface Design: Adopts arc transitions (≥0.5mm radius) to eliminate polishing dead zones. 0.1°-0.2° draft angles are incorporated for long splines to prevent surface scratches during demolding.
Polishing Process Adaptation: Reserves 0.02-0.03mm polishing allowance, avoiding deep grooves/narrow gaps. AO-grade (Ra0.008μm) polishing requires initial surface roughness ≤Ra0.4μm.
Demolding Mechanism: Uses 2-3mm diameter ejector pins (3-5 units, uniform distribution) with 0.002-0.003mm cavity clearance to prevent melt overflow.
Design balances nitrided layer performance and structural strength:
Nitrided Layer Thickness: 0.2-0.3mm for metal stamping molds and 0.3-0.4mm for high-temperature alloy molding. Critical stress areas (e.g., core roots) feature 1-2mm thickened walls to avoid brittle fracture.
Ventilation System Optimization: 0.03-0.05mm deep × 5-8mm wide vents ensure gas evacuation, avoiding bubbles and material shortages.
High-Temperature Adaptation: 0.015-0.02mm cavity clearance compensates for thermal expansion. High-temperature alloy locating pins maintain positioning accuracy.
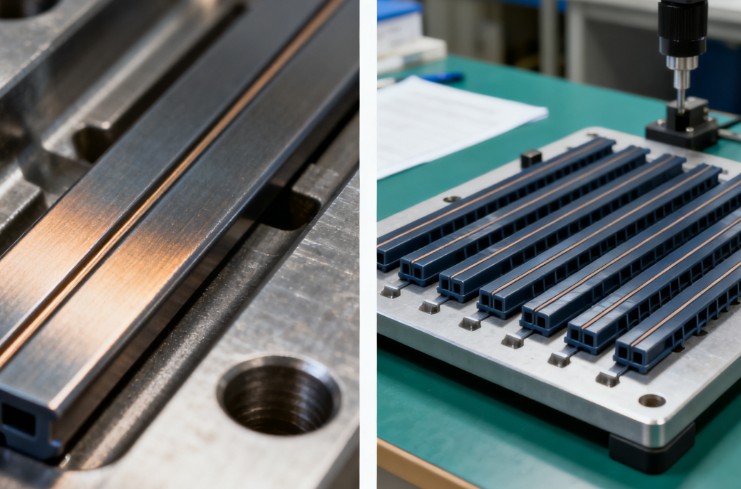

Polishing Molds: Ideal for polymer material testing (e.g., consumer electronics casings, daily chemical packaging, medical plastics) requiring high surface quality.
Nitrided Molds: Suitable for metal/high-temperature alloy testing (e.g., automotive steel stamping, aerospace alloy molding, power battery pole pieces) under harsh conditions.
Prioritize polishing molds for surface quality-focused polymer testing; choose AO Grade for optical applications and A1 Grade for general appearance testing.
Select nitrided molds for high-temperature/high-wear metal testing, with 0.3-0.4mm layers for severe wear scenarios.
Opt for single-cavity molds for small-batch high-precision testing and multi-cavity molds for large-scale production (3-5x efficiency improvement).
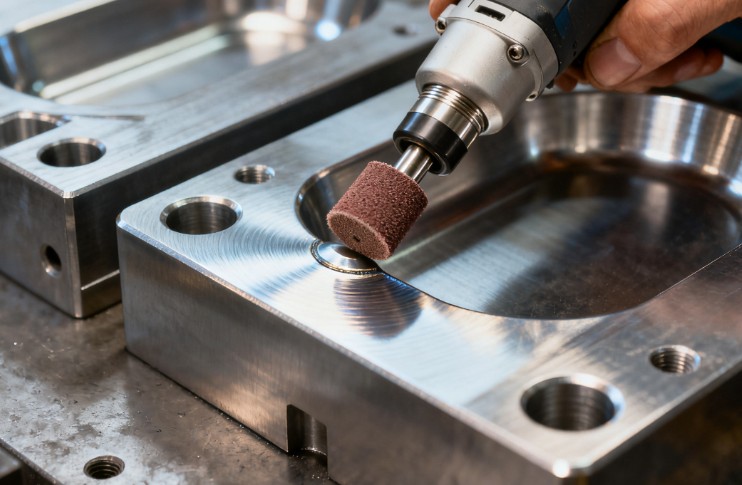

Polishing Molds: CNC rough machining (±0.05mm tolerance) → EDM semi-finishing (Ra1.6μm) → progressive polishing (180#-1000# oilstones → 220#-1500# sandpaper → 9μm-1/4μm diamond paste). Assembly requires 0.001-0.002mm guide pillar clearance.
Nitrided Molds: Degreasing (50-60℃ alkaline cleaner) → derusting (10-15min phosphoric acid soak) → plasma nitriding (500-560℃, 10-15L/min ammonia flow, 4-6h holding) → finish grinding (±0.01mm tolerance). Assembly reserves 0.01-0.015mm thermal expansion clearance.
Pre-Use: Preheat polishing molds to 50-80℃ and nitrided molds to 100-120℃. Control injection pressure (10-15MPa for polishing, 15-20MPa for nitriding) and holding time (5-10s for polishing, 10-15s for nitriding).
Daily Maintenance: Clean polishing mold cavities with anhydrous ethanol; conduct monthly hardness testing for nitrided molds (re-nitriding if HRC < 55).
Storage: Apply volatile rust inhibitor for polishing molds and high-temperature rust inhibitor for nitrided molds. Store in 40%-60% humidity and 15-25℃ environment.
Factory Inspection: Test surface roughness (white light interferometer), dimensional accuracy (CMM), and demolding performance (50 consecutive cycles) for polishing molds. Verify nitrided layer thickness (metallographic microscope), hardness (Vickers hardness tester), and corrosion resistance (72h salt spray test) for nitrided molds.
In-Service Inspection: Comprehensive testing every 1,000 cycles; document material type, molding parameters, and maintenance records for traceability.
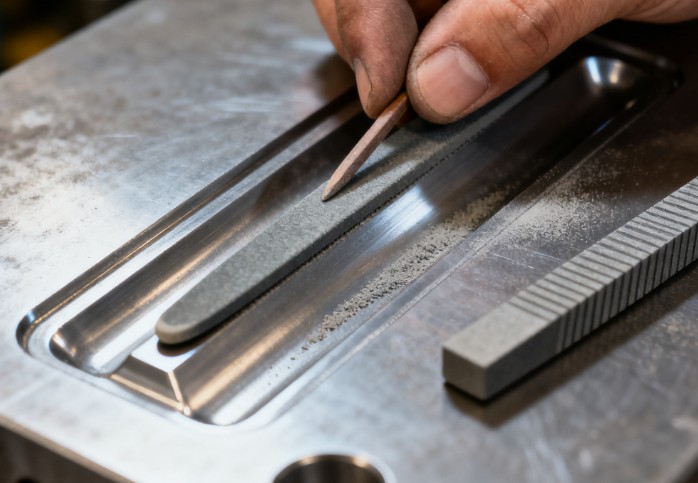

The industry is evolving toward high precision, green manufacturing, and intelligence:
High Precision: Nanopolishing technologies (e.g., magnetorheological polishing) achieve Ra0.001μm surfaces. Composite nitriding (nitriding + PVD coating) boosts hardness to HV3000+.
Green Manufacturing: Abrasive-free polishing (e.g., laser polishing) reduces wastewater by over 60%. Low-temperature plasma nitriding (450-500℃) cuts energy consumption by 30%.
Intelligence: Digital twin technology optimizes polishing/nitriding parameters. Sensor-equipped molds enable real-time condition monitoring, reducing failure rates by 40% via AI-driven maintenance predictions.
Future development will focus on adapting to new materials (e.g., graphene composites, titanium alloys) and extreme conditions, advancing flexible polishing molds for soft materials and ultra-high-temperature nitrided molds for ceramics, supporting the upgrading of precision manufacturing industries.





