Cold Working MoldCold working molds, like thick - plate punching dies, endure high impact loads at normal temperature, along with friction and wear. Thus, materials need high toughness to resist repeated shocks and prevent cracking. Sufficient hardness is also crucial as it ensures good wear resistance, keeping the tool edge sharp. For instance, Cr12MoV cold work die steel, used in automotive girder steel plate punching, maintains its cutting edge well due to its high toughness and hardness, even after numerous operations.
Hot Working MoldHot - work molds, such as die - casting molds, face harsh conditions. They operate at high temperatures (up to several hundred degrees Celsius), experiencing alternating thermal and mechanical stresses, oxidation, corrosion, and direct contact with high - temperature liquid metal. The chosen material must have good high - temperature strength to maintain mechanical properties, excellent thermal fatigue performance to resist cracking during thermal expansion and contraction, and good oxidation and corrosion resistance. H13 steel, commonly used in aluminum alloy die - casting molds, has low strength loss at high temperatures, resists thermal fatigue cracking, and withstands the corrosion of aluminum alloy liquid.
Plastic MoldFor injection molds in plastic molds, they contact plastic melt and bear pressure and friction, with some having high surface - quality requirements. So, materials need good corrosion resistance (as different plastics have varying corrosiveness), appropriate hardness and wear resistance to maintain shape and accuracy, and good polishing properties for high - quality plastic products. P20 steel is suitable for processing polycarbonate injection molds as it has corrosion resistance, moderate hardness, and is easy to process and polish.
Cutting ProcessingDuring cutting, a material with a hardness in the HB170 - 250 range is ideal. If too hard, tool wear accelerates and cutting force increases, affecting accuracy; if too soft, chips don't break easily and scratch the surface. High vanadium high - speed steel is hard to machine due to high hardness, while low - carbon steel has better cutting performance but needs to meet surface - quality requirements. For simple - shaped molds, free - cutting materials can be used for rough machining, followed by heat treatment to adjust hardness for finishing.
ForgingMaterials with a wide forging temperature range are favorable for forging. It allows for better control of the forging process and reduces forging defects. Low - alloy steels, for example, have a wide forging temperature range. Good plasticity and low deformation resistance are also important. Good plasticity enables plastic deformation, and low deformation resistance reduces the required forging equipment capacity. Pure aluminum has excellent plasticity and low deformation resistance. For mold steel, alloying elements' effects on plasticity and deformation resistance must be considered.
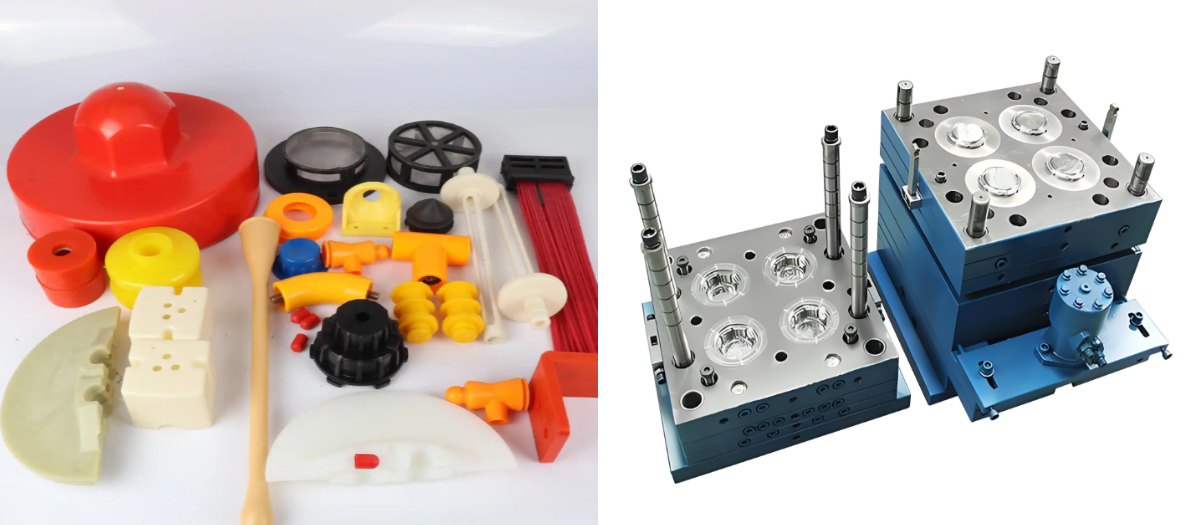

Heat TreatmentIn heat treatment, materials should have appropriate hardenability to achieve the required hardness after quenching, good hardenability for uniform mold performance, and strong tempering stability. T10 steel has good hardenability but may not be suitable for large molds. CrWMn steel, with better hardenability, is suitable for complex - shaped, large - sized cold working molds, and its properties are reasonable after tempering.
Malleable Temperature Range Factors
A wide malleable temperature range is crucial for forging. It provides temperature adjustment space, enabling operators to control forging parameters like deformation amount and forging times, reducing defects. Low - alloy steels, for example, allow for flexible forging process arrangements.
Plastic and Deformation Resistance Factors
Material plasticity and deformation resistance affect forging performance. Good plasticity facilitates plastic deformation, and low deformation resistance reduces the need for high - power forging equipment. Pure aluminum is easy to forge due to its high plasticity and low deformation resistance. For mold steel, alloying elements' effects on these properties must be considered for optimal forged blank quality.
Forging Crack Sensitivity Factors
Materials with low forging crack sensitivity are less likely to crack during forging, ensuring forging blank quality. New die steels with optimized alloy composition and structure have reduced crack sensitivity, improving forging pass rates.
Hardness Influencing FactorsMaterial hardness impacts machining performance. High - hardness materials accelerate tool wear and increase cutting force, while low - hardness materials cause chip - breaking problems. When cutting hard alloy dies, high - hardness tools and careful parameter selection are needed.
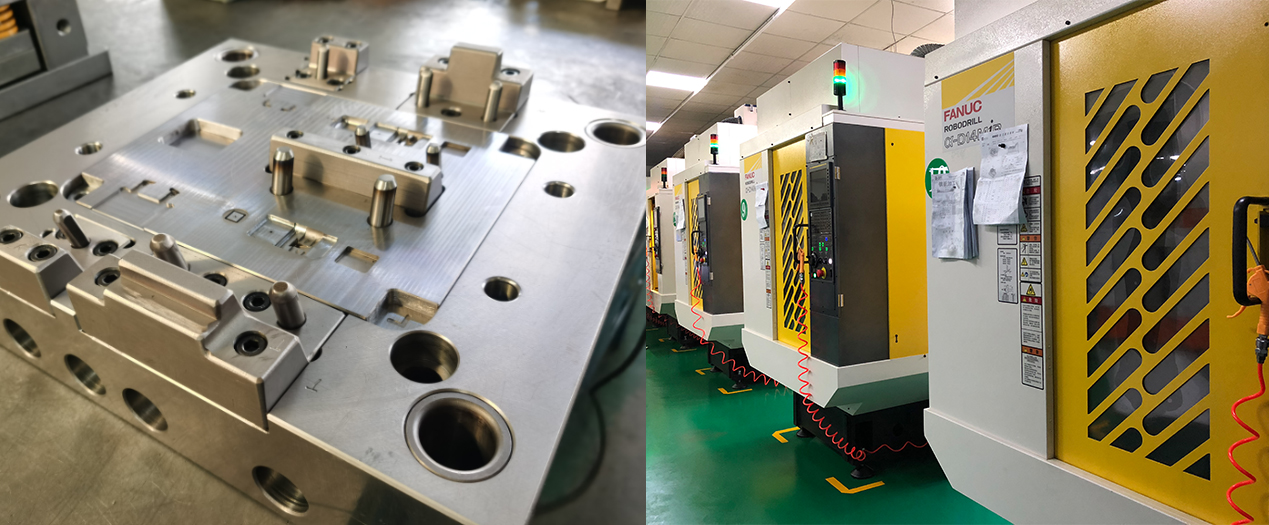

Influencing Factors of Organizational StructureMaterial structure affects machining. Non - uniform structures with hard points can damage tools and affect surface roughness. Alloy steels with carbides require special tools and processes.
Influencing Factors of ToughnessMaterial toughness is related to machining. Materials with too much toughness produce long, unbreakable chips, while those with too little toughness may be brittle. Moderate - toughness materials ensure smooth cutting and good surface quality.
When selecting mold materials, price is important. Choose relatively inexpensive materials that meet performance and process requirements. For simple, low - requirement small molds, common carbon tool steel suffices, avoiding unnecessary costs.
The stability and adequacy of material resources matter. Materials should have wide sources and stable market supply to ensure timely procurement and prevent production delays. Imported high - end materials with unstable supply may not be suitable for projects with strict production schedules; domestic alternatives can be considered.
Don't focus solely on initial material cost; consider mold service life. High - quality materials may have high initial costs but can lower unit - product costs over the long term. High - quality hot work die steel for die - casting molds, despite high procurement costs, offers good long - term economic benefits due to its excellent properties. Weigh initial cost and service life to select cost - effective materials.




